Cardiac surgery, commonly referred to as heart surgery, is a specialized procedure performed by experienced heart specialists. These surgeries aim to restore normal heart functions, repair damaged heart structures, and prevent serious complications.
Understanding the various types of heart surgery, the procedures involved, what to expect before and after, and the recovery process can help patients make informed decisions and actively participate in their treatment and recovery.
What Is Cardiac Surgery?
Cardiac surgery addresses structural or functional issues within the heart and its blood vessels. It includes both traditional open-heart surgeries and minimally invasive techniques. A heart specialist will assess each patient’s unique situation to determine the best approach, considering factors like the specific condition, age, and overall health.
Heart surgery not only treats existing problems but also helps prevent future complications, such as heart attacks or sudden heart failure. A thorough understanding of these surgeries helps patients prepare mentally and physically for the treatment journey.
Why Is Heart Surgery Performed?
Surgery is often recommended for issues such as coronary artery disease, heart valve disorders, congenital heart defects, severe arrhythmias, and end-stage heart failure. The primary goal is to restore proper heart function, improving both long-term health and quality of life.
When Is Heart Surgery Needed?
A heart specialist may recommend surgery if a patient experiences persistent symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or fluid retention, especially if these persist despite medication. Early surgical intervention can prevent further complications and significantly improve survival rates.

What Conditions Are Treated With Heart Surgery?
A heart specialist will evaluate these conditions and recommend the most suitable surgical approach for each patient.
1. Coronary artery disease: Blockages that restrict blood flow to the heart.
2. Heart valve disorders: Problems with the heart valves that affect circulation.
3. Congenital heart defects: Structural issues present at birth.
4. Cardiomyopathy: A disease that affects the heart muscle and its pumping capability.
5. Severe arrhythmias: Life-threatening heart rhythm disorders.
How Common are Heart Operations?
Heart surgery is a common practice worldwide, with procedures like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and valve replacement being the most frequent. Thanks to advancements in technology, skilled heart surgeons, and improved post-operative care, these procedures have become safer and more effective. However, every patient receives a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific heart condition and overall health.
Types of Cardiac Surgery
Cardiac surgery includes several specialized procedures, each designed to address specific heart conditions. Understanding the various types of heart surgery can help patients have informed discussions about their treatment options with their heart specialist.
1. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG):
CABG restores blood flow to the heart by bypassing damaged arteries using healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body. This procedure relieves chest pain, prevents heart attacks, and improves heart function, potentially involving one to four bypasses, depending on the number of blocked arteries.
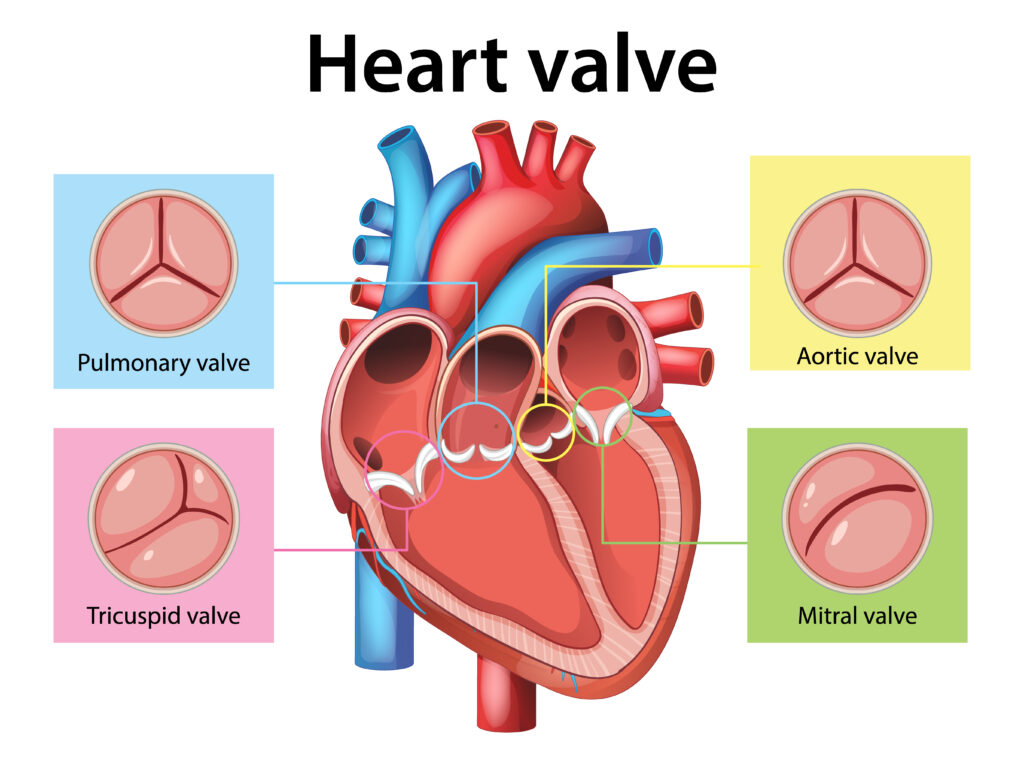
2. Heart Valve Surgery:
This procedure repairs or replaces damaged heart valves, including the aortic, mitral, tricuspid, or pulmonary valves. Valve repair aims to preserve as much of the patient’s natural tissue as possible, while replacement may involve mechanical or biological valves to restore normal blood flow.
3. Congenital Heart Defect Surgery:
Corrective surgeries address heart defects present at birth, like septal defects (holes in the heart) or valve malformations. These surgeries can be performed in children or adults, depending on the severity of the defect and its impact on heart function.
4. Heart Transplant Surgery:
Heart transplant surgery is for patients with end-stage heart failure, where a diseased heart is replaced with a healthy donor heart. The process includes meticulous pre-surgical evaluations, matching, and lifelong post-transplant care, including immunosuppressive therapy.
5. Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery (MICS):
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery (MICS) uses small incisions and specialized tools for procedures like valve repair or bypass. Benefits include reduced pain, lower risk of infection, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery. Robotic-assisted techniques may also be utilized in some cases.
Methods Used in Cardiac Surgery
The surgical method chosen depends on individual patient needs and health status. A cardiovascular doctor will determine the most effective and safest approach.
1. Open-Heart Surgery:
This traditional method involves opening up the chest to access the heart directly. A heart-lung machine is typically used to maintain blood circulation during the surgery.
2. Off-Pump (Beating Heart) Surgery:
Performed without stopping the heart, this technique allows certain types of heart bypass surgery while the heart continues beating. This potentially reduces risks associated with traditional approaches.
3. Minimally Invasive and Hybrid Techniques
Hybrid procedures involve small incisions, catheter-based approaches, or robotic assistance. Such surgical methods aim to minimize trauma, improve precision, and shorten recovery time while still achieving the same surgical goals as traditional open-heart surgery.
Heart Surgery Procedure Overview (Open-Heart Surgery)
This overview gives a general guide of what happens during the open-heart surgery. This gives patients a clear picture of the whole process.
- Anesthesia and Surgical Incision
Patients receive general anesthesia, ensuring they are unconscious and free of pain. A careful incision is made to access the heart, with attention to minimizing tissue damage.
- Use of the Heart-Lung Machine
The heart-lung machine temporarily takes over the functions of circulation and oxygenation, allowing surgeons to work on a still heart.
- Repair or Surgical Correction
Surgeons perform the needed repairs, bypasses, or replacements, utilizing precise preoperative imaging and continuous monitoring during the operation.
- Weaning Off the Bypass Machine
Post-surgery, as the heart regains normal function, patients are gently disconnected from the heart-lung machine while ensuring consistent circulation.
- Chest Closure and Monitoring
After completing the surgery, the chest is closed, and patients are moved to the intensive care unit for ongoing monitoring of heart function, oxygen levels, and vital signs.
What Happens Before Heart Surgery?
A thorough assessment is essential before heart surgery to guarantee safety and effectiveness. This involves medical evaluations, diagnostic tests, and discussions with the surgical team to help patients feel prepared and lessen anxiety.
Pre-Surgical Tests and Evaluation
Patients must undergo extensive evaluations, including blood tests, ECGs, echocardiograms, coronary angiography, and imaging studies to determine surgical risk and to accurately plan the procedure.
How to Prepare for Heart Surgery
Preparation may encompass medication adjustments, fasting, preoperative counseling, lifestyle changes, and mental readiness to minimize anxiety and enhance outcomes.
What to Expect During Hospital Admission
Admission for cardiac operation entails preoperative preparations, safety checks, and guidance for patients and families to ensure everything runs smoothly.
Before the Surgery Day
Patients receive preoperative instructions, evaluations, and monitoring to confirm readiness. Family members are informed about hospital protocols and what to expect post-surgery.
On the Day of Surgery
The surgical team conducts last-minute checks, administers anesthesia, and assures patient safety before beginning the procedure, with nursing staff providing support and reassurance.
What Happens After Heart Repair Surgery?
Preparation is key. Patients meet with their heart specialists and undergo assessments to ensure they are physically and mentally prepared for the surgery.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Patients are monitored closely in the ICU to stabilize heart rhythm, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and overall condition.
Pain Management After Heart Surgery
Pain is managed through medications and supportive care, promoting comfort and early mobility.
Medications Prescribed After Surgery
Patients might receive blood thinners, medications to support heart function, and pain relief medications to facilitate a safe recovery.
Recovery Guide After Heart Repair Surgery
Recovery is a gradual process that involves both physical and emotional support. Structured rehabilitation and monitoring facilitate complete healing and assurance of safe return to daily routines.
Hospital Recovery (5-7 Days)
Initial recovery focuses on monitoring vital signs, managing pain, and starting gentle mobility and breathing exercises.
Home Recovery Phase (Weeks 1-4)
Patients slowly increase their activity levels, adhere to dietary recommendations, and care for their wounds, with family support being vital.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Program (6-12 Weeks)
Supervised exercise, education, and counseling aid in regaining cardiovascular strength, minimizing risk factors, and adopting sustainable heart-healthy habits.
Full Recovery and Return to Daily Life
Most patients can resume regular activities within a few months, based on their overall health and adherence to medical advice.
Precautions During Recovery
Patients should avoid heavy lifting, follow dietary guidelines, attend all follow-ups, and monitor for any warning signs such as unusual swelling or chest discomfort.
Benefits and Risks of Heart Surgery
Heart surgery offers significant benefits but also carries potential risks. Understanding these allows patients to make informed decisions and discuss realistic expectations with their surgeons.
Advantages
- Improved heart function and blood flow
- Relief from chest pain, breathlessness, and fatigue
- Prevention of future heart attacks and heart failure
Possible Risks and Complications
- Infection or bleeding
- Irregular heartbeat or arrhythmias
- Blood clots or stroke
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
A thorough discussion with a cardiac surgeon helps weigh the benefits against the potential risks.
Recovery Outlook and Long-Term Results
The long-term success of heart surgery depends on recovery, ongoing care, and lifestyle changes. Patients can expect gradual improvement, but proactive follow-up is essential.
Recovery Timeline and Expected Progress
Recovery varies by procedure and patient factors but generally progresses through hospital care, home recovery, rehabilitation, and long-term lifestyle management.
Survival Rate
Modern heart repair surgery has high survival rates, especially for routine procedures like CABG and valve repair.
Life Expectancy After Heart Surgery
Many patients resume active lifestyles and enjoy long-term heart health following successful surgery.
Long-Term Heart Care
Regular check-ups, medication adherence, a healthy diet, and exercise are essential for sustained heart health.
Advanced Technologies Used in Modern Heart Repair Surgery
Modern heart surgery uses advanced technology to improve outcomes, reduce complications, and shorten recovery. These tools also allow surgeons to perform more precise and minimally invasive procedures.
Robotic-Assisted Heart Surgery
Robotics allows precision in delicate repairs with minimal tissue disruption.
Catheter-Based Minimally Invasive Procedures
Small tubes and cameras enable complex procedures without a whole chest opening.
Hybrid Operating Rooms
These combine surgical and interventional capabilities for complex, multi-step procedures.
Heart-Lung Machine (Cardiopulmonary Bypass)
Ensures safe circulation and oxygenation during open-heart surgeries.
Who Is the Right Candidate for Heart Surgery?
Heart surgery is recommended based on the severity of the condition, symptoms, and overall patient health. A thorough evaluation helps identify patients most likely to benefit safely.
Which Patients Are Advised to Undergo Heart Surgery?
Candidates include patients with
- Advanced disease
- Structural heart defects
- Persistent symptoms
- Poor response to medications
Surgeons carefully assess overall health, age, and comorbidities before recommending surgery.
Role of the Cardiac Anesthesiologist
The cardiac anesthesiologist is a vital member of the surgical team. They manage anesthesia, monitor vital signs, and ensure patient safety during surgery, while also helping plan post-operative pain management and recovery strategies.
When Should You See a Cardiac Surgeon?
Recognizing warning signs and consulting a cardiac surgeon early can improve surgical outcomes and reduce risks.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
- Persistent chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath or fatigue
- Swelling in the legs or feet
- Dizziness, fainting, or palpitations
Expert Cardiac Surgical Care with Dr. Ghulam Sarwar
Dr. Ghulam Sarwar provides advanced surgical care for complex heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, valve disorders, and congenital defects. His approach combines expert evaluation, precise surgical planning, and comprehensive follow-up, prioritizing patient safety, communication, and long-term outcomes.
When to Seek a Surgical Consultation
If you or a loved one has been advised to consider heart surgery, or if symptoms persist despite treatment, early consultation can clarify options and improve outcomes. You can schedule a consultation with Dr. Ghulam Sarwar, available from Monday to Saturday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM at Omar Hospital, Johar Town, Lahore (Pakistan) to discuss your condition, surgical options, and a personalized treatment plan.
